What is Protein Energy Malnutrition?
Protein energy/ calorie malnutrition (PEM/ PCM), the foremost public health obstacle, is characterized by the deficiency of either protein or energy in the body leading to wasting and stunting along with severe effects on tissues and other metabolic functions leading to growth retardation. According to World Health Organization (WHO), the variation among the nutrient’s consumption, expenses, supply and demand to ensure the necessary growth for survival. PEM is classified in different ways. The acute PEM with the deprivation of energy only is termed as mild PEM. The chronic PEM with the deficiency of protein only is referred as moderate PEM. The acute as well as chronic PEM characterized by the deficiency of protein along with calories is labelled as severe PEM.
“PEM is quoted as myriad of morbidity. Geographically, more than 70% of PEM children live in Asia”…. WHO
Notable Facts!
- Globally, PEM targets every fourth child: 26.7% are underweight, while 32.5% are stunted (WHO).
- 5.6 million Under-five mortality is because of malnutrition (UNICEF).
- Nearly 852 million malnourished people live in developing countries (FAO).
- 51% of preschools have PEM in Pakistan (UNICEF).
- Bangladesh is the home of stunting due to malnutrition.
- In India, the mortality rate of children is 2.1 million.
- About 47.2% and 28.5% of Srilankans are underweight and stunted, respectively.
- 45.57% of Nepalese children were stunted and 52.46% were underweight.
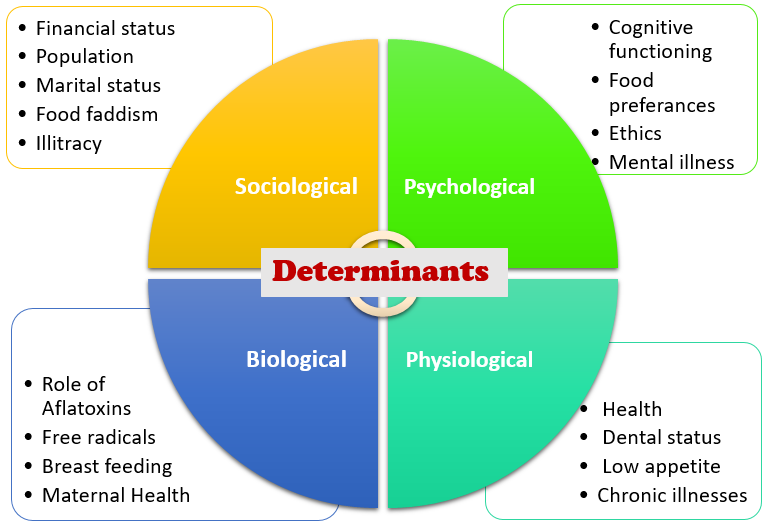
Recommendations:
Children are one of the vulnerable groups of PEM, so priority must be given to them regarding nutrition. Health care programs, training sessions and companies should be conducted to educate the families and mothers on the control and prevention of PEM. The provision of necessary education, proper feeding practices, health facilities, nutritious food should be assured. Skill-based interventional programs, food fortification programs, supplementary programs, and breastfeeding programs will be helpful in this regard. Gender equality, religious as well as cultural equity, food security, breastfeeding, personal hygiene, employment, population-control and equal distribution of food are the key parameters to ensure positive health status. To ensure this, all the stakeholders, government as well as non-government officials and representing bodies have to work together in the best possible way.



